Introduction
Cloud computing enables businesses and individuals to access vast amounts of computing resources without the need for physical infrastructure. This blog will explore the fundamentals of cloud computing, its various models, deployment strategies, benefits, challenges, and future trends.
What is Cloud Computing?
Definition
Instead of owning physical servers or data centers, users can access these resources on a pay-as-you-go basis from cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Key Characteristics
- On-Demand Self-Service
- Broad Network Access
- Resource Pooling
- Rapid Elasticity
- Measured Service
Challenges of Cloud Computing
Security and Privacy
Data security is a significant concern with cloud computing. Organizations must ensure their data is protected from breaches and unauthorized access.
Downtime and Reliability
Cloud services can experience downtime, affecting business operations. Reliable cloud providers with robust SLA agreements can mitigate this risk.
Compliance and Legal Issues
Different countries have varying regulations on data storage and transfer. Organizations must ensure they comply with relevant legal requirements.
Cloud Deployment Models

Public Cloud
A public cloud is a cloud infrastructure offered to multiple clients by a cloud provider. It is owned and operated by a third party, delivering computing resources like servers and storage over the internet.
Advantages
Scalability: Resources can be scaled quickly to meet demand.
Private Cloud
A private cloud is a cloud infrastructure dedicated solely to one organization, offering greater control and security. Keywords: Private cloud, Dedicated infrastructure, Security.
Advantages
- Enhanced Security: Offers higher levels of control and security.
- Customization: More customizable to specific organizational needs.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud is an integrated cloud environment that uses a mix of on-premises private cloud and third-party public cloud services with orchestration between the two platforms.
Advantages
- Flexibility: Balances between on-premises infrastructure and cloud.
- Optimized Workloads: Distributes workloads across both environments based on requirements.
Types of Cloud Computing Services
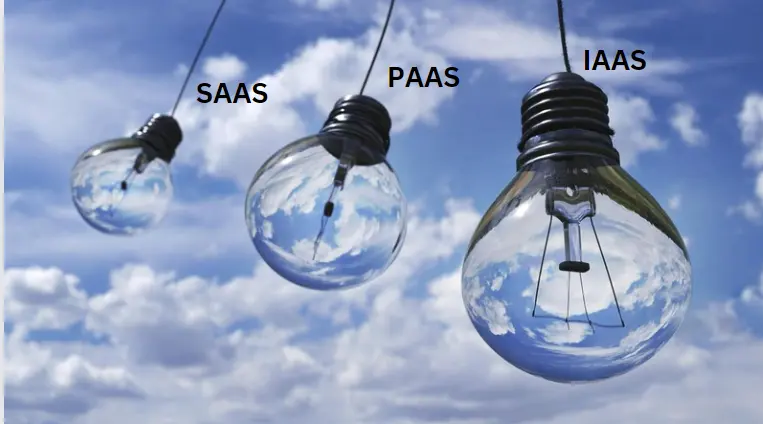

Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. Users can rent virtual machines, storage, and networks, which are managed by the cloud provider.
- Examples
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): Offers a wide range of IaaS Solutions.
- Microsoft Azure: Provides scalable virtual machines and storage options.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Notable PaaS providers include Heroku, Google App Engine, and Microsoft Azure App Services.
- Examples
- Heroku: A cloud platform that supports several programming languages and helps developers deploy and manage applications.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Common SaaS applications include Google Workspace, Microsoft Office 365, and Salesforce.
- Examples
- Salesforce: A CRM platform that provides tools for sales, customer service, and marketing.
- Microsoft Office 365: A suite of productivity applications available online.
Benefits of Cloud Computing

Cost Efficiency
Cloud computing reduces the need for investing in physical hardware and managing data centers. Pay-as-you-go models help organizations save costs.
Scalability and Flexibility
Organizations can quickly scale resources up or down based on demand, ensuring they have the necessary resources without over-provisioning.
Disaster Recovery
Cloud computing offers robust disaster recovery solutions, ensuring data is backed up and easily recoverable.
Collaboration and Accessibility
Cloud services enable team collaboration from anywhere in the world, as long as there is internet access. Applications and data are accessible 24/7.
Future Trends in Cloud Computing

Edge Computing
Edge computing processes data closer to the data source rather than in a centralized data center. This trend is expected to grow, reducing latency and bandwidth usage.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Cloud providers are increasingly integrating AI and machine learning capabilities into their services, enabling more advanced data analysis and automation.
Multi-Cloud Strategies
Organizations are adopting multi-cloud strategies, using services from multiple cloud providers to avoid vendor lock-in and enhance reliability.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is transforming the IT landscape, offering scalable, flexible, and cost-effective solutions for businesses and individuals. Understanding the different models and deployment strategies helps in making informed decisions. While cloud computing presents numerous benefits, it also comes with challenges that must be managed. As technology evolves, trends like edge computing, AI integration, and multi-cloud strategies will shape the future of cloud computing. Embracing these advancements will be crucial for staying competitive in an increasingly digital world.
